
In the Variable value field, type a path to the log file. Under Variable name, type the following: SSLKEYLOGFILE You can also create the variable under System variables if you’d like to log SSL keys for every user on the system, but I prefer to keep it confined to my profile. On the Advanced tab, click the Environment Variables button.Ĭlick the New… button under User variables. Next, click Advanced system settings on the list to the left.

Start by right-clicking on My Computer, and selecting Properties from the menu. This variable, named SSLKEYLOGFILE, contains a path where the pre-master secret keys are stored. In Windows systems, you’ll need to set an environment variable using the Advanced system settings utility. When you’re finished, you’ll be able to decrypt SSL and TLS sessions in Wireshark without needing access to the target server. Here are the steps to decrypting SSL and TLS with a pre-master secret key: Your browser can be made to log the pre-master secret key, which Wireshark uses to decrypt SSL and TLS sessions. It’s the current standard in cryptography and is usually implemented via Diffie-Hellman. Using a pre-master secret key to decrypt SSL in Wireshark is the recommended method.Ī pre-master secret key is generated by the client and used by the server to derive a master key that encrypts the session traffic. Using a pre-master secret key to decrypt SSL and TLS See also: Wireshark Alternatives for packet sniffing When Wireshark is set up properly, it can decrypt SSL and restore your ability to view the raw data. SSL encryption makes using Wireshark more challenging because it prevents administrators from viewing the data that each relevant packet carries. Note: In this guide, I’ll mostly be referring to SSL as a catchall term for SSL and TLS, its successor. It uses various encryption methods to secure data as it moves across networks. SSL is an encryption protocol that operates on the Transport layer of the OSI model. Using Wireshark, you can look at the traffic flowing across your network and dissect it, getting a peek inside of frames at the raw data. Specifically, it captures frames – the building blocks of packets – and lets you sort through and analyze them. Wireshark is a network traffic analyzer it’s a core utility that many administrators use to troubleshoot problems on their networks.

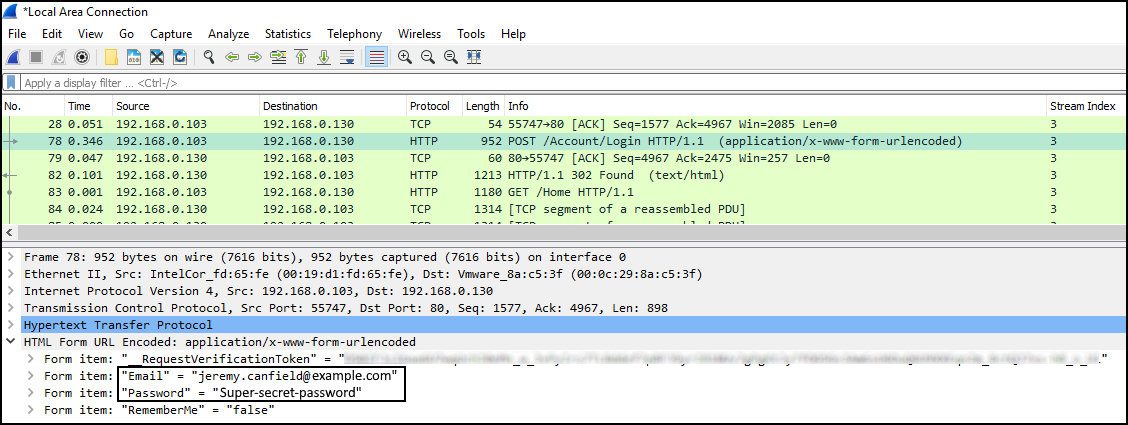
If you’ve ever tried using Wireshark to monitor web traffic, you’ve probably run into a problem – a lot of it is encrypted transmissions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
